The Comprehensive Guide to Barcode Readers and Their Impact on Business
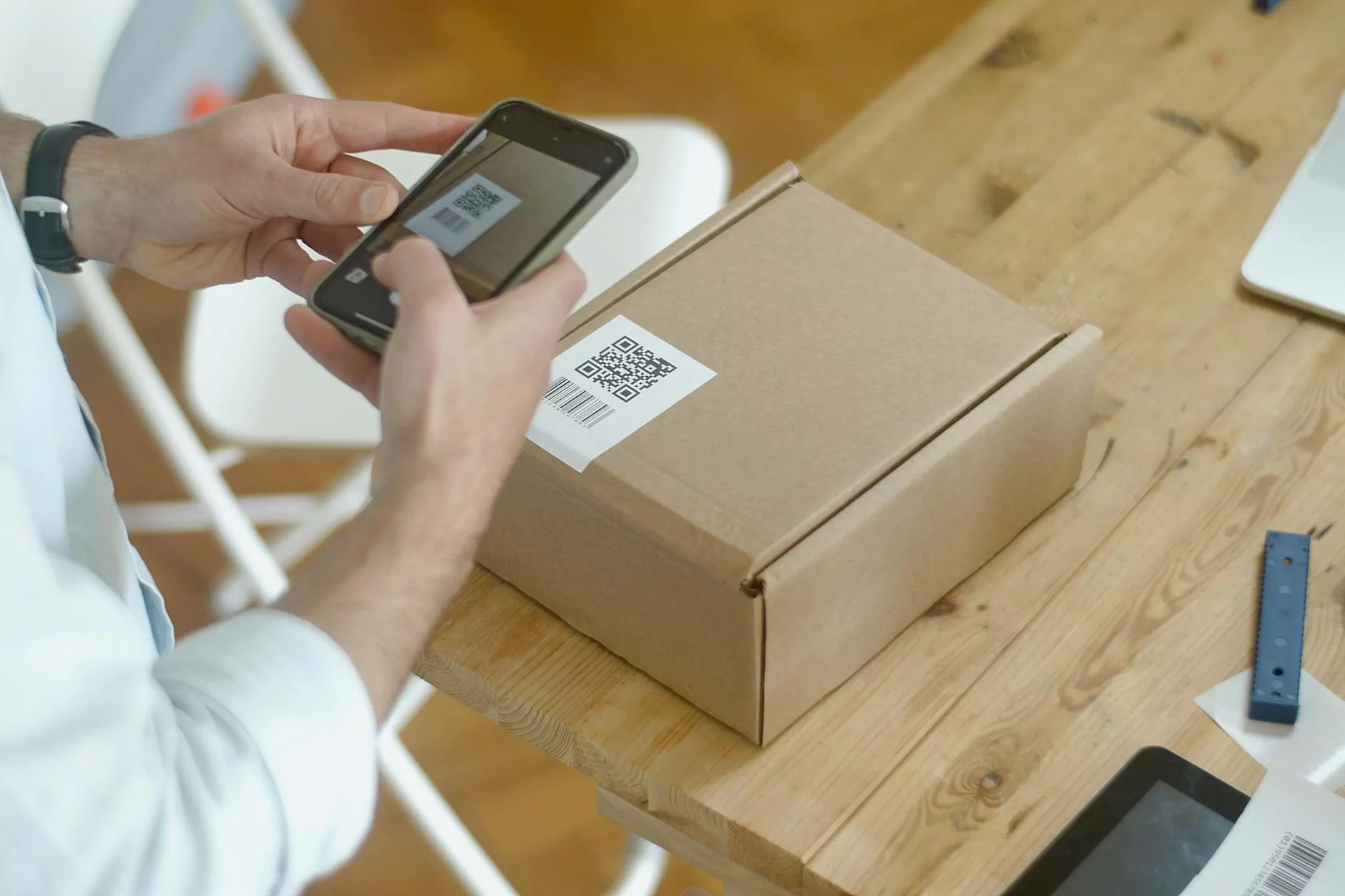

Barcode readers are essential tools in modern business operations, revolutionizing the way products are tracked and managed. Their effectiveness spans across various industries, from manufacturing and retail to healthcare and logistics. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of barcode readers, discussing their functionality, benefits, and the myriad of applications that highlight their importance in today's fast-paced marketplace.
What is a Barcode Reader?
A barcode reader, also known as a barcode scanner, is a device that uses a laser or camera to decode the information embedded in the barcode. This information typically includes product details, pricing, and identification codes. The technology behind barcode readers has evolved significantly, making them indispensable in streamlining operations, reducing human error, and enhancing overall efficiency.
How Barcode Readers Work
Barcode readers function by using light sensors to scan and interpret patterns found in barcodes. These patterns consist of a series of vertical lines and spaces that represent data. The process generally follows these steps:
- Scanning: The reader emits a beam of light, usually in the form of a laser. This light reflects off the barcode.
- Decoding: The reflected light is captured by the reader's sensor. The variations in light intensity are translated into a digital signal, which is then decoded into meaningful data.
- Output: Finally, the decoded data is sent to a computer or system, enabling further processing or action – for example, updating inventory or sales records.
Types of Barcode Readers
There are several types of barcode readers, each designed for specific applications:
- Handheld Barcode Scanners: These are portable devices commonly used in retail environments. They allow employees to scan items quickly and efficiently.
- Fixed-Mount Barcode Scanners: Typically installed at checkout counters or conveyor belts, these scanners automate the scanning process for higher throughput.
- Mobile Computers: These are handheld devices that combine a barcode reader with a portable computer, ideal for field operations or warehousing.
- Stationary Scanners: Used in manufacturing settings, these scanners can read barcodes from products on a production line.
- 2D Barcode Scanners: Capable of reading QR codes and data matrix codes, these scanners have become increasingly important for marketing and information dissemination.
Benefits of Using Barcode Readers in Business
The adoption of barcode readers offers businesses a multitude of advantages:
- Improved Accuracy: Manual data entry is prone to errors, but scanning barcodes significantly reduces mistakes, ensuring data integrity.
- Increased Efficiency: With barcode scanners, the checkout and inventory processes are significantly faster, enhancing customer satisfaction and optimizing workflow.
- Inventory Management: Barcode systems allow for real-time tracking of stock levels. Businesses can monitor inventory more accurately, reducing the chances of overstocking or stockouts.
- Cost Reduction: Operating costs can be lowered through increased efficiency and reduced wage expenses as fewer staff are required for inventory management.
- Enhanced Reporting: Barcode systems provide analytics that help businesses make data-driven decisions regarding inventory, sales, and customer behaviors.
Applications of Barcode Readers Across Various Industries
Barcode readers find applications across numerous sectors:
1. Retail Industry
In retail, barcode readers facilitate quick checkouts, reduce lost sales due to pricing errors, and enhance inventory control. Retailers can easily monitor which products are selling well and adjust their stock accordingly.
2. Healthcare Sector
In healthcare, barcode technology is used to track patient medication, monitor equipment usage, and ensure the correct patient receives the correct treatment. This enhances safety and compliance with healthcare regulations.
3. Warehousing and Logistics
In warehouses, barcode readers are critical for tracking inventory movement. They expedite receiving, storing, and shipping processes, ultimately leading to faster delivery times and improved customer service.
4. Manufacturing
Manufacturers use barcode systems to track raw materials and finished goods throughout the production process, maintaining quality control and efficient workflow.
5. Food Industry
Food producers and retailers utilize barcode technology to ensure freshness and traceability, which are critical in managing product recalls and ensuring consumer safety.
Choosing the Right Barcode Reader for Your Business
When selecting a barcode reader, consider the following factors to ensure it meets your business needs:
- Type of Barcode: Determine whether you need to read standard 1D barcodes or 2D barcodes like QR codes.
- Read Range: Assess how far the scanner needs to be from the barcode; some scanners are designed for close-range use, while others can read from a distance.
- Connectivity: Choose between wired or wireless options based on your operational setup and preference.
- Durability: If the scanner will be used in rugged environments, select a model built to withstand rough handling.
- Integration: Ensure the barcode reader can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems such as inventory management software.
The Future of Barcode Technology
The landscape of barcode technology continues to evolve with advancements such as mobile scanning apps and cloud-based solutions. Here are some trends shaping the future:
- Increased Adoption of Mobile Scanners: Smart devices equipped with scanning capabilities enable quicker and more versatile operations.
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) is allowing for more connected systems where barcode readers can communicate with other devices for enhanced data management.
- Use of Augmented Reality: Augmented reality (AR) applications are emerging, allowing enhanced interaction with products via QR codes, providing customers with more information.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As businesses focus on sustainability, digital barcodes and apps are being promoted to reduce paper waste associated with traditional labels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, barcode readers offer transformative benefits for businesses in every sector. By investing in barcode technology, organizations can achieve enhanced efficiency, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction. As technology progresses, businesses that leverage barcode readers effectively will remain competitive and drive innovation in their industries. For businesses looking to streamline their operations, embracing barcode technology through reliable suppliers like Durafastlabel can be a strategic move towards operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between 1D and 2D barcode scanners?
1D barcode scanners read traditional barcodes consisting of vertical lines, whereas 2D scanners can read square patterns like QR codes, containing more data.
2. Do I need software to utilize a barcode reader?
Yes, most barcode readers require compatible software to manage the data collected, which can integrate with your existing business systems.
3. Can barcode readers be used in the field?
Absolutely! Many barcode readers are portable and designed for field use, ensuring that work can be efficiently performed outside of a traditional office environment.
4. What industries benefit the most from barcode technology?
Industries such as retail, healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and food services greatly benefit from the efficiency and accuracy that barcode technology provides.
5. Where can I find high-quality barcode readers?
Reliable suppliers such as Durafastlabel offer a range of high-quality barcode readers suitable for various business applications.